Sympathetic nerve: A part of the autonomic nervous system that raises blood pressure and heart rate under stress, constricts blood vessels, and dilates the pupil, or related to it. The autonomic nervous system controls a person's blood pressure and keeps it within limits. Blood pressure is controlled by regulating vascular tone, water drainage, and heart rate. In addition, which parts of the autonomic nervous system are activated when blood pressure is low? Prolonged hypertension can affect vision (hypertensive retinopathy) and reduce the blood supply to the legs. It can cause stroke, bleeding from large blood vessels (aneurysm of the aorta), and chronic kidney disease (hypertensive nephropathy). High blood pressure also forms blood clots in the arteries leading to the brain, blocking blood flow and potentially stroke. dementia. When arteries narrow or become blocked, blood flow to the brain is restricted, which can lead to certain types of dementia (vascular dementia). What Causes High Blood Pressure? High blood pressure usually develops over time. This can be caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as inadequate regular physical activity. Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and obesity, can also increase your risk of developing high blood pressure.
The neurological regulation of blood pressure and blood flow depends on the cardiovascular center in the medulla oblongata. This cluster of neurons responds not only to changes in blood pressure, but also to blood levels of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen ions. The center of the cardiovascular system contains three different pairs of components.
How does the autonomic nervous system regulate blood pressure?
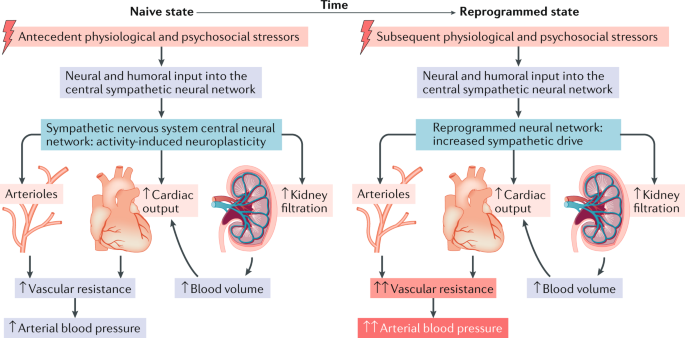
The autonomic nervous system and its sympathetic nerves play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure. Their role in short-term regulation of blood pressure through the 1–3 pressure reflex mechanism, especially in response to transient changes in arterial pressure, is well known.
How does high blood pressure affect the body?
High blood pressure affects the eyes, kidneys and nervous system. At very high blood pressure (180 or 200 mm Hg), blood vessels in the brain rupture, damaging parts of the brain.
How does high blood pressure affect the brain?
Very high blood pressure (& gt; 180 or 200 mm. Hg) causes blood vessels in the brain to rupture, damaging parts of the brain. This can lead to sudden paralysis of one side of the face or body, resulting in visual impairment, speech loss, and loss of consciousness. Neurological problems depending on the part of the brain affected.
What are the main causes of high blood pressure?
President of the American Neuroorthopedic Association Some people feel that high blood pressure is caused by vascular disease, heart (heart) or kidney problems. In addition to all of the above, we feel that the central nervous system is the cause. Sympathetic and parasympathetic channel disorders.
Which part of the nervous system regulates blood pressure?
The autonomic nervous system and its sympathetic nerves play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure. Their role in short-term regulation of blood pressure, especially in response to transient changes in arterial pressure through pressure reflex mechanisms, is well known.
Which nervous system causes high blood pressure?
The sympathetic nervous system plays an important role in the regulation of arterial pressure and increases. Sympathetic nervous system activity is associated as a major precursor to hypertension in both human and animal disease models. ..
How does hypertension affect the autonomic nervous system?
Hypertension is associated with abnormalities in autonomic nervous system (ANS) function, increasing sympathetic output and reducing parasympathetic tone. Lifestyle interventions are at the forefront of the treatment of hypertension, and reduced blood pressure (BP) effects may be associated with altered ANS function.
Below you will find two helpful answers on a similar topic. 👇
How do I identify a nest?Do sponges walk or swim?
