Like all insects, the ant's body is divided into three main parts: the head, chest, and abdomen. Ants have a hard, waterproof exoskeleton made of a material called chitin. They are very strong due to their size: they can lift 10 times their own weight! Most ants have two large compound eyes.
What are the internal organs of ants?
Brain. The ant's brain is a ganglion, quite different from the one you or I have. A nerve-fiber knot above the esophagus but behind the pharyngeal part of the intestine. .. esophagus. .. Pharyngeal gland. .. muscle. .. chest. .. heart. .. Other parts of the ants. .. abdomen. Internal anatomy of ants-Inside ants-Ant's nest in Milm
Do ants have internal organs?
Despite its small size, ants rely on both internal and external organs to perform their required biological functions. .. Ants have some organs that are similar to human organs, as well as some organs that are different from the inside of the human body.
Can ants survive without a stomach?
Abdominal deprived worker ants sometimes run at high speeds, continue to care for young people in their nests, fight themselves and other species of aliens, and aren't aware of their loss for a few days? It may behave like this. .. Formica subsericea workers lived for 5 days without abdomen.
Do ants have blood?
The simple answer is that ants have something similar to blood, which scientists call "blood lymph". .. Blood turns red because it contains many small packages called "red blood cells." This package carries oxygen around the body. Ants and other insects also have fluids in their bodies that move nutrients.
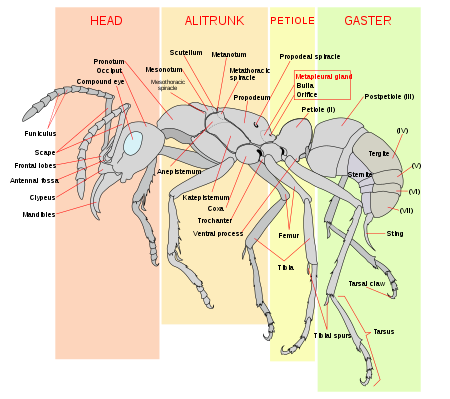
Below you will find two helpful answers on a similar topic. 👇
Do ants have muscle tissue?What type of legs do ants have?
