Typical examples of hedging include wheat farmers and wheat futures markets. Farmers sow seeds in the spring and sell their harvest in the fall. In the meantime, farmers are exposed to the price risk of lower wheat prices in the fall.
What is a hedge?
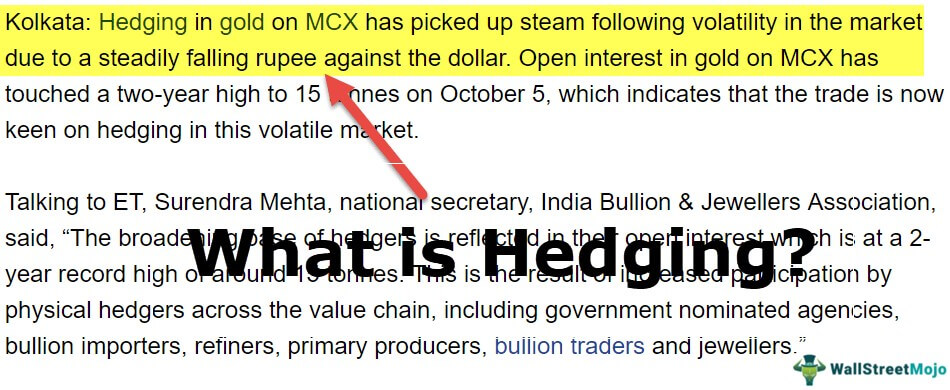
Hedging is an investment made to mitigate the risk of adverse price fluctuations in an asset. Hedges usually consist of offsetting or opposition to the relevant securities.
What is a perfect hedge with an example?
A hedge that accurately offsets the profit or loss from an existing investment position. An example of a full hedge is the short-term sale of your securities to fix existing profits and transfer them to the next tax year. .. See also risk hedging.
What are the three common hedging strategies?
Depending on the asset or asset portfolio to be hedged, there are several effective hedging strategies to mitigate market risk. The three most popular are portfolio building, options and volatility indicators.
What are hedges and their types?
Hedging Strategy Types Forward Contract: A contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specific price on a specific date. .. Futures Contract: This is a standard contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at an agreed price and quantity on a specified date.
Below you will find two helpful answers on a similar topic. 👇
What is your hedgehog concept?What is the word hedge means?
