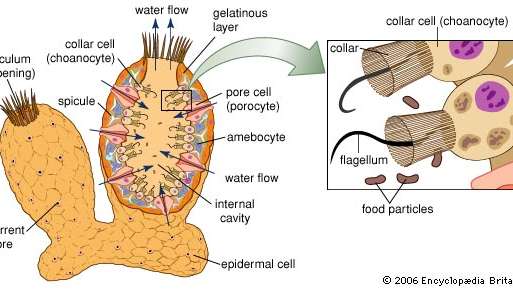
Sponges are rare animals in that they do not have a clear organ to perform various functions. The most important structure is a canal and chamber system called the water flow system, where water circulates and carries food and oxygen to the sponge. Structure and function of the sponge The sponge is the ectoderm, which originates from two basic germ layers, the ectoderm (outer layer) and the endoderm (inner layer). Most sponges are asymmetric. Asymmetry means that if an animal is split into two halves along any axis, the halves will not be equal or identical. Remember that sponges are alive and attached to the seabed. They are called stemless because they are attached. To get food, sponges allow water to pass through their bodies in a process known as filter feeding. Water is drawn into the sponge through a small hole called the inflow hole. The sponge uses many collar cells to generate an electric current that draws water into the pores. Each cell has a whip-like structure called the flagella and collar. The choanocytes line the channels and chambers inside the sponge and generate an electric current that draws water into the sponge by shaking the flagella back and forth all at once. Choanocytes are specialized to perform this function of generating an electric current. (See Figure / Cross Section of Tissue) Sponges are rare animals in that they lack clear organs to perform various functions. The most important structure is a canal and chamber system called the water flow system, where water circulates and carries food and oxygen to the sponge.
What is the structure of the sponge?
The structure of the sponge is simple. One end is attached to a solid such as a rock and the other end is called an oscrum. Open to the environment. Sponge can obtain microorganisms such as algae and bacteria as food from the opening. Some sponges are carnivorous and use spicules to capture small crustaceans.
Do sponges have special cells?
Special cells: Sponge has special collar cells (or collar cells) that are unique in the animal kingdom. They have a bristles, whip-like structure and act to set the water flow so that the sponge can sift food particles from the water.
How does a sponge filter water?
Special cells: Sponge has special collar cells (or collar cells) that are unique in the animal kingdom. They have a bristles, whip-like structure and act to set the water flow so that the sponge can sift food particles from the water. Water enters through the suction hole and exits from the sponge through the exhalation hole.
What is the function of the water flow of the sponge?
Forms and features. The most important structure is a canal and chamber system called the water flow system, where water circulates and carries food and oxygen to the sponge. The water flow system also helps disperse gametes and larvae and remove waste products.
What gives the sponge a structure?
They have a flagellar, whip-like structure that acts to set the water flow so that the sponge can sift food particles from the water. .. Skeleton: Many species produce a silica (silica) or calcium carbonate (calcium) skeleton, providing some structure for an essentially shapeless growth morphology.
What is important about sponges?
Sponge is important in the nutrient cycle of the coral reef system. .. This process reduces excess nitrogen levels in coral reefs and prevents harmful ecosystem changes. Scientists say that converting nitrogen gas to useful nitrogen is also beneficial to the survival of other organisms in the area.
What do most sponges have to do to maintain their shape?
The sponge has no organized tissue, but it relies on special cells such as choanocytes, porosites, amoebic cells, and pinacosites for its special functions in the body. Mesohyl acts as a kind of endoskeleton and helps maintain the tubular shape of the sponge.
What kind of body structure does the sponge have?
Cell typeThe body of the sponge is hollow, kept in shape by the collagen-based jelly-like substance mesohyl, and reinforced by a dense network of fibers also made of collagen. The inner surface is lined with choanocytes, which are cells with a cylindrical or conical collar that surrounds one flagella for each choanocyte.
Below you will find two helpful answers on a similar topic. 👇
What are the characteristics of the demosponges?What are the physical characteristics of a rabbit?
