
Prionotus evolans
FAMILY
Triglidae
TAXONOMY
Prionotus evolans Linnaeus, 1766, North or South Carolina,
United States.
OTHER COMMON NAMES
French: Grondin volant; Spanish: Rubio volador.
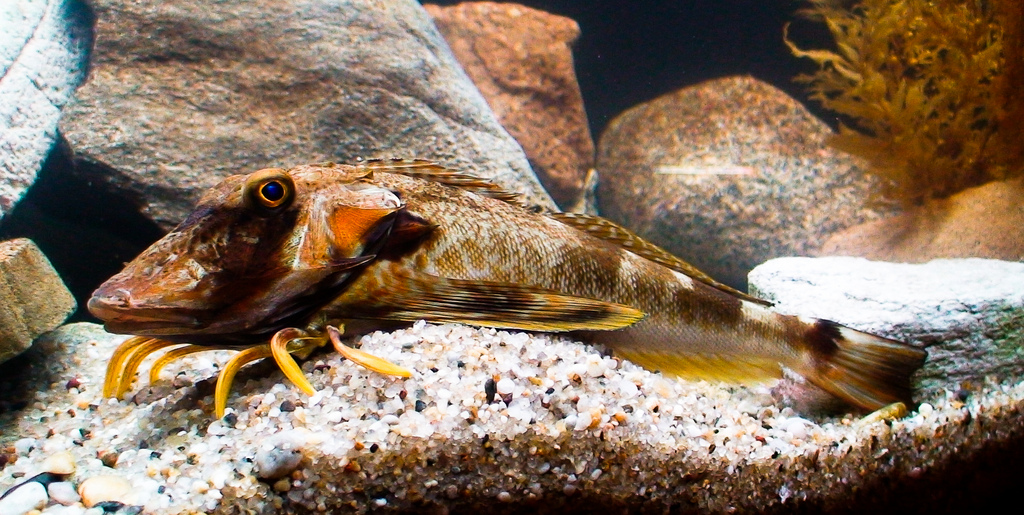
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
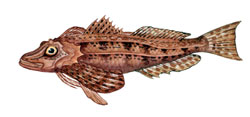
Reaches 17.7 in (45 cm) maximum length. Characterized by a
large bony head with many ridges and spines and a bifurcate
lateral line on the tail. The striped sea robin is white ventrally,
with various shades of golden, brown, and orange on the sides
and dorsal surface. It often has dark saddles underneath the
dorsal fins and is best distinguished from other species by the
two thin, black stripes running along the side of the body. The
dorsal stripe runs the entire length of the fish along the lateral
line, and the smaller, incomplete stripe is situated below. The
tail has two black bars with a light area between them.
DISTRIBUTION
Found from southern Nova Scotia down the Atlantic Coast of
North America to northeastern Florida. Typically collected at
depths of less than 200 ft (61 m) but have been found at depths
as great as 550 ft (168 m).
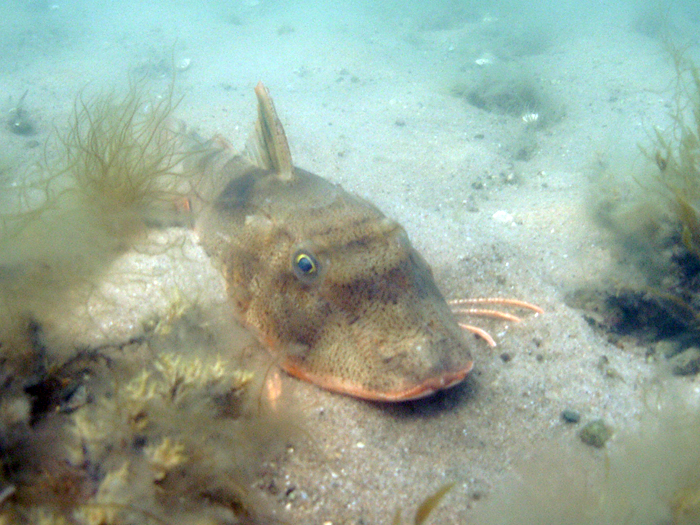
HABITAT
Usually found on sandy bottoms. It often can be taken in inshore
estuaries or over reefs, particularly in summer months.
BEHAVIOR
The striped sea robin uses its free pectoral rays to “walk”
along the seafloor in search of prey. The sea robins along
the Atlantic Coast of North America are famous for their
ability to produce sounds by “beating” the swim bladder
muscles against the gas-filled swim bladder, making a characteristic
grunting noise. Typically, the striped sea robin is
found offshore, but the species makes migrations into the
deeper, more saline estuaries for breeding. This species is
not venomous.
FEEDING ECOLOGY AND DIET
The diet consists mainly of crustaceans, mollusks, and fishes.
Preyed upon by larger predatory fishes.
REPRODUCTIVE BIOLOGY
Produces pelagic eggs. This species appears to breed in deeper
estuarine environments, typically in the summer months from
May to October. It seems clear that sound plays a role in
choice of mate.
CONSERVATION STATUS
Not listed by the IUCN.
SIGNIFICANCE TO HUMANS
The striped sea robin is a commercially important fish. It is
collected and used for human consumption, fishmeal, bait, pet
food, and fertilizer. Smaller specimens often are collected for
the aquarium trade, though they grow too large for most home
aquaria.
Photo Gallery of - Striped sea robin




 Animalia Life
Animalia Life