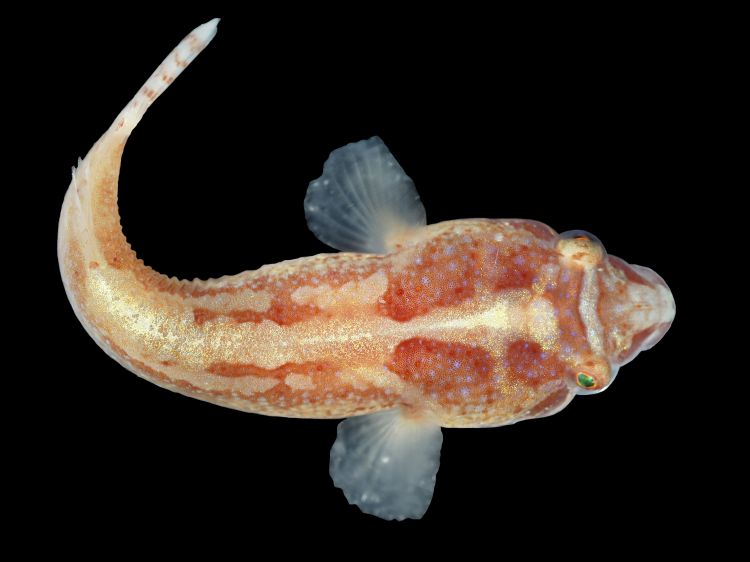

Diplecogaster bimaculata bimaculata
FAMILY
Gobiesocidae
TAXONOMY
Diplecogaster bimaculata bimaculata Bonnaterre, 1788, seas of
England, although no types were designated.
OTHER COMMON NAMES
English: Two-spotted sucker.
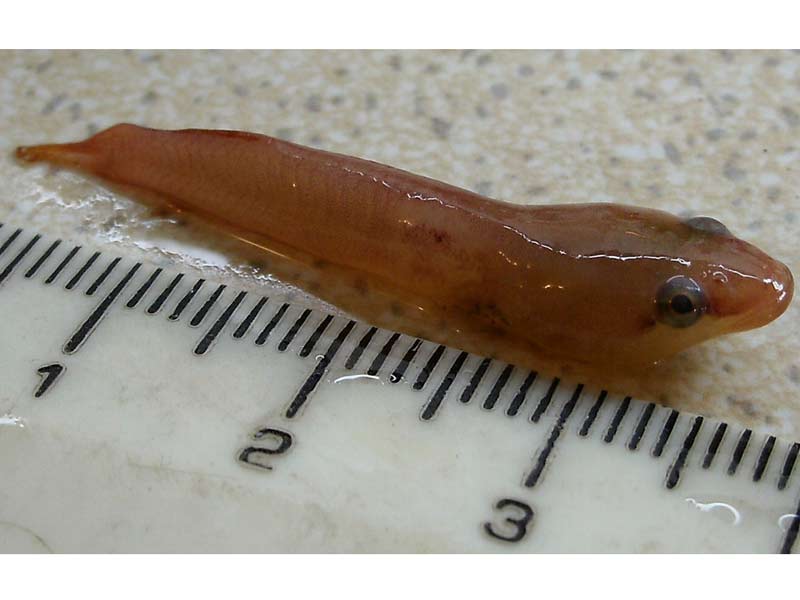
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Flattened and elongated body, with a somewhat triangular
snout. The dorsal fin has 4–7 soft rays, and the anal fin has
4–7 soft rays. The gill opening is minute. Color varies but usually
is red with yellow on the ventral surface and a pattern of
blue and brown spots over the body surface. Males are distinguished
by a purple or red spot, ringed in yellow, on each
flank, behind the pectoral fins. Grows to 2.4 in (6 cm) in
length.
DISTRIBUTION
Eastern Atlantic Ocean, from Norway and the Faroe Islands
south to Gibraltar and the western Mediterranean and Adriatic.
The subspecies Diplecogaster bimaculata euxinica is found in the
Black Sea and D. bimaculata pectoralis from the offshore Canary
and Cape Verde Islands and the Azores.
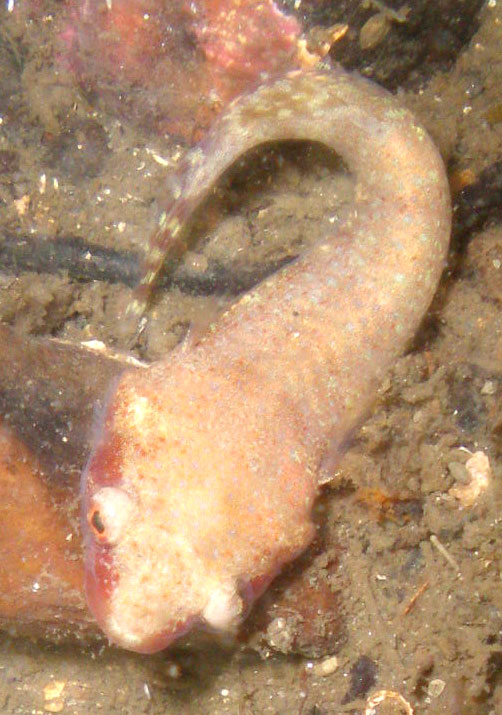
HABITAT
A temperate species found on sea grass beds, rocky bottoms,
bivalve banks, and mud bottoms. Reported to favor shells.
Depths range between 59 and 180 ft (18–55 m) in cooler waters
and down to 328 ft (100 m) in the warmer Mediterranean.
BEHAVIOR
Not well known. Males likely are territorial.
FEEDING ECOLOGY AND DIET
Feeds on small benthic invertebrates.
REPRODUCTIVE BIOLOGY
Demersal courtship and spawning occur in the spring and summer
months, with golden-colored eggs laid in masses under
shells or stones. Males provide most of the parental care. Larvae
are planktonic.
CONSERVATION STATUS
Not listed by the IUCN.
SIGNIFICANCE TO HUMANS
Occasionally recovered from trawls working soft mud bottoms
or bivalve banks.
Other popular Animals
Photo Gallery of - Two-spotted clingfish




 Animalia Life
Animalia Life