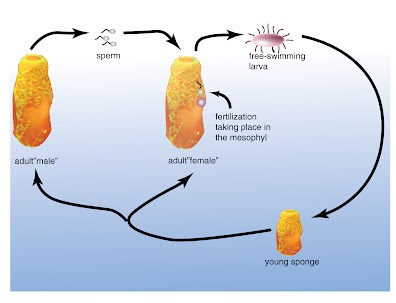
The typical life cycle of a freshwater sponge can consist of five stages that can be repeated several times a year. The vegetative growth phase is followed by blast formation (asexual reproduction) or sexual reproduction, cryptobiosis (resting phase), precursor cell hatching, and finally regeneration.
What is the general body plan for sponges?
The most basic body plan is called asconoid. In asconoid sponges, two major cell layers surround a liquid-filled cavity called the sponge coil, which is the large central cavity of the sponge.
What is the sponge breeding process?
Sponges can propagate sexually and asexually by budding using gametes. The sponge is hermaphroditic, but an individual creates only one type of gamete at a time. There are two forms of asexual reproduction that the sponge can pass through: external budding and internal budding.
What is a precursor cell? And why is it important to the sponge life cycle?
Precursor cells are internal buds found in sponges and are involved in asexual reproduction. It is a mass of asexually reproduced cells that can grow into a new organism, the adult sponge.
How long does it take for the sponge to mature?
When harvesting sponges, sponge divers cut each sponge by hand to make sure that at least 1 inch of the base remains intact. After that, the sponge will return to its original shape within 3-5 years.
Below you will find two helpful answers on a similar topic. 👇
Why do rabbits have peg teeth?What kind of front teeth do rabbit have how do they help them?
