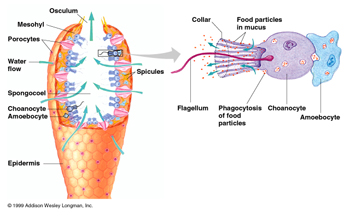
There is no heart, no veins, no arteries, and no blood on the sponge. However, they achieve gas exchange and nutrient consumption through the movement of water. Water is drawn into the sponge through the inner choanocytes, and the inner choanocytes take up water from the outer pores of the sponge. However, the reason why the human heart cannot regenerate after a heart attack is due to the cells that make up the heart tissue (Beltrami et al. 2001). The findings indicate that human cardiomyocytes proliferate rapidly during the fetal period, but replication of these cells diminishes shortly after birth (Soonpaa and Field 1997). Since they do not have special tissues, they do not show the characteristics of multicellular organisms, excitatory tissues, they do not develop the nervous system. This is a strategy adopted by some sponges, so such sponges are not considered multicellular organisms. Not all sponges are as simple as this. Basic anatomy. The sponge does not even contain organs or tissues. Instead, they consist of three cell-sized layers. Compressed polygonal cells called pinacosites make up the outer sac layer, the pinacorder. The cells in the outer layer can move inward and change their functions.
Why does the sponge have no heart?
The sponge has entered the sponge phylum of the animal kingdom. Animals in this kingdom lack organs such as the digestive system, nervous system, circulatory system and organ system of the body. Therefore, they also lack the heart. They take their nutrients from the stream of water flowing through their bodies.
Why doesn't my heart regenerate?
If the heart is damaged and the cardiomyocytes die, the remaining cardiomyocytes will regenerate and the heart will be able to regenerate. Researcher FAU has found a possible explanation for why this does not happen to humans.
Why are sponges not considered multicellular organisms?
This is a strategy adopted by some sponges, so such sponges are not considered multicellular organisms. All sponges are so simple and not have some degree of differentiation in cell function.
What is the structure of the sponge?
Sponges (Sponge phylum) are aquatic animals. From an anatomical point of view, these are some of the simplest multicellular organisms that do not have differentiated organs, but have different cell layers (tissues) that perform different functions in the body.
Why does the sponge have no heart lungs or nervous system?
The simplest animals, such as sponges (Porifera) and rotifers (Rotifera), because diffusion allows for the proper exchange of water, nutrients, waste, and dissolved gas, as shown in Figure 1a. Does not require a circulatory system. ..
Why are there no organs on the sponge?
Unlike protozoa, sponges are multicellular. However, unlike higher metazoans, the cells that make up the sponge are not organized into tissues. Therefore, the sponge lacks true tissue and organs. Moreover, they have no body symmetry.
Why don't sponges need organs to survive?
The sponge does not have true sensory organs, so it cannot hunt prey. Fortunately, they don't have to travel to find food. .. These cells are equipped with small tentacles called flagellas that sway back and forth to draw water into the body of the sponge.
What's in the sponge?
I have no head or legs. Internally, there are no brains, stomachs or other organs. This is because the sponge evolved much faster than other animals. In fact, the sponge has a true tissue. March. 2019г.
Below you will find two helpful answers on a similar topic. 👇
What do you call a person born blind?Do sponges have a brain?
